What is problem solving?
Problem-solving entails a systematic process whereby experts within the organization identify the root causes of issues and propose optimal solutions. Key factors considered in selecting solutions include profitability, elimination of problem factors, cost-effectiveness, expedited results, resource efficiency, and other pertinent criteria.
The process of problem-solving
The problem-solving process consists of 5 steps as follows, which can be different from one organization to another. In general, this process follows a special approach called the continuous improvement cycle (PDCA), which includes the following 4 steps:
Planning;
Implementing;
Controlling;
Acting;
Step 1: Defining the problem
At this stage, the relevant team identifies and evaluates the problem through the organization’s quality management system inputs, which include process performance monitoring results, customer feedback, quality non-conformance, internal and external audit results, non-fulfillment of goals, and plans.
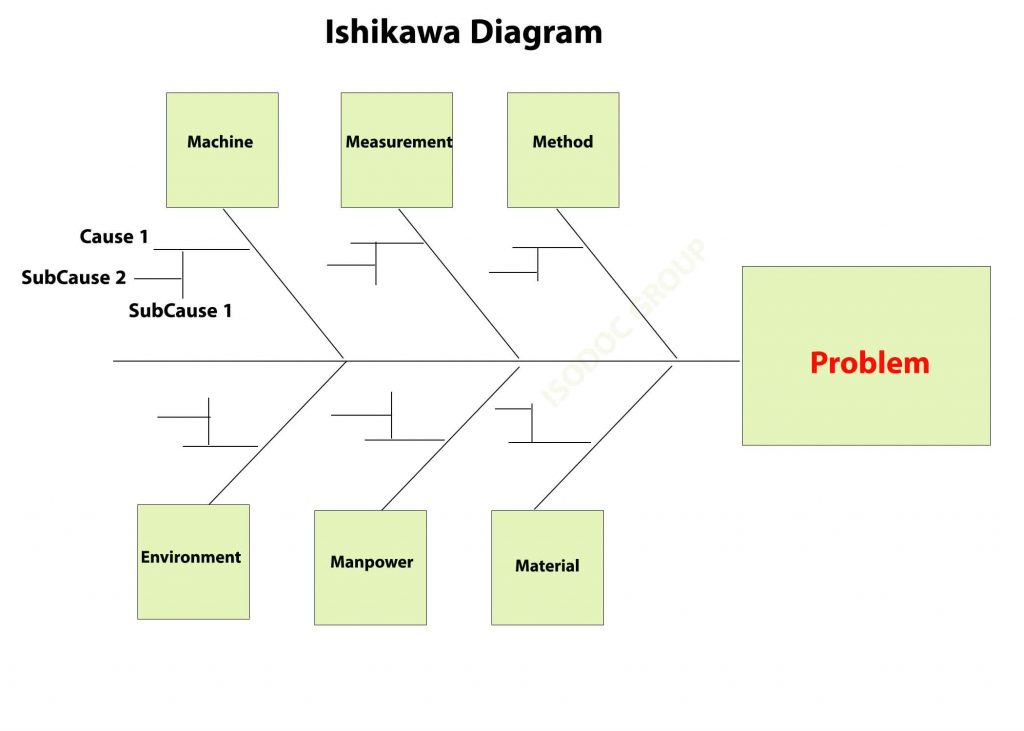
Step 2: Rooting the problem
At this stage, the team tries to find the root cause of the problem with techniques such as the Ishikawa model (Fishbone Diagram) or 5 whys, there may be more than one cause, and the technical team must identify and select the root cause that has a more significant impact on creating problems.
Step 3: Determine solutions
Identifying and selecting problem solutions is the process by which the team determines the best solutions with the following techniques:
- Many benefits;
- It takes less time to run;
- Less consumption of resources;
Usually, problem-solving does not have only one solution, and a problem may have several solutions, so teams must choose the best solution that meets certain criteria.
Step 4: Action plan
When the solution to the problem is determined, the organization’s experts provide a plan for the implementation of actions, which includes the following:
- activities;
- start time;
- end time;
- Required resources;
- Responsible for implementation;
- Acceptance criteria;
- Program progress percentage;
- Goal achievement percentage;
Step 5: Control of actions
As the last step and in order to ensure the achievement of the desired problem-solving goals, the project manager periodically measures and controls the actions taken.
Conclusion
Organizations must turn problem-solving into a systematic approach, and this requires senior managers to believe in achieving big goals in its implementation.
